Enhance SMB efficiency with our ERP solutions. Streamline operations and boost productivity for small and medium-sized businesses.
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) need to keep up with the ever-increasing demand for efficiency, productivity, and data management.
This is where SMB ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems come into play. These powerful tools are transforming the way SMBs operate, enabling them to compete with larger enterprises and streamline their operations.
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) need to keep up with the ever-increasing demand for efficiency, productivity, and data management.
This is where SMB ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems come into play. These powerful tools are transforming the way SMBs operate, enabling them to compete with larger enterprises and streamline their operations.
Introduction to SMB ERP
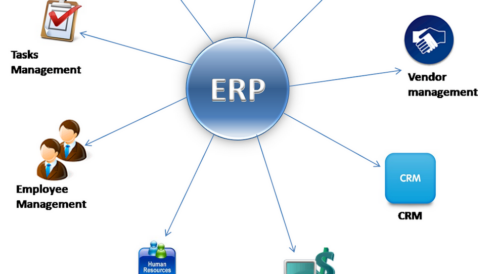
SMB ERP, or Small and Medium Business Enterprise Resource Planning, is a software solution designed to manage and integrate various aspects of a business, including finance, human resources, inventory, procurement, and more.
Unlike traditional ERP systems that are often too complex and expensive for smaller companies, SMB ERP is tailored to meet the unique needs and budget constraints of SMBs.
The Importance of ERP for Small and Medium Businesses
Implementing an ERP system is crucial for SMBs looking to thrive in today’s competitive market. It provides a centralized platform for data management, automates routine tasks, and offers real-time insights into business operations. This empowers SMBs to make informed decisions, reduce operational costs, and deliver a superior customer experience.
Key Features and Benefits of SMB ERP
Key Features:
Integrated Modules: SMB ERP integrates various functions like accounting, inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), and more into a single system.
Real-time Data: Access to real-time data ensures accurate decision-making.
Customization: SMB ERP solutions can be tailored to meet specific business needs.
Scalability: They can grow with your business, accommodating increased demand.
Benefits:
Improved Efficiency: Streamline processes and reduce manual errors.
Enhanced Productivity: Automate repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on strategic activities.
Data Security: Protect sensitive business data.
Competitive Advantage: Stay ahead of the competition with data-driven insights.
Types of SMB ERP Solutions
There are various SMB ERP solutions available, ranging from cloud-based to on-premises systems. The choice depends on your specific needs and resources.
Cloud-based SMB ERP: Offers flexibility, scalability, and accessibility from anywhere.
On-premises SMB ERP: Provides control and security over your data but requires more extensive infrastructure.
Cloud-based SMB ERP:
Definition: Cloud-based SMB ERP systems are hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet. They offer flexibility, scalability, and accessibility from anywhere.
Advantages:
Accessibility: Users can access the system from anywhere with an internet connection, making it ideal for remote work.
Scalability: Cloud-based ERP solutions can easily grow with your business, accommodating increased demand.
Cost-Efficiency: Often, they have lower upfront costs, as you don’t need to invest in on-premises infrastructure.
Considerations:
Security: Data security and privacy are critical when using cloud-based ERP, so ensure the provider has robust security measures in place.
On-Premises SMB ERP:
Definition: On-premises ERP systems are installed and run on your company’s servers and infrastructure. They offer control and security over your data.
Advantages:
Control: You have full control over the system and your data, which can be advantageous for certain industries with strict regulations.
Customization: On-premises ERP systems often allow for more extensive customization to fit your specific business processes.
Data Privacy: You have direct control over your data, which can enhance data privacy.
Considerations:
Upfront Costs: On-premises solutions typically involve higher upfront costs, including hardware and software purchases.
Maintenance: You are responsible for maintenance, updates, and security, which can be resource-intensive.
Hybrid SMB ERP:
Definition: Hybrid ERP solutions combine elements of both cloud-based and on-premises systems. This approach offers the flexibility of cloud solutions while maintaining some data on-site for security or regulatory compliance.
Advantages:
Flexibility: A hybrid approach allows you to choose where to store certain data, providing a tailored solution to meet your unique needs.
Scalability: You can scale specific aspects of your ERP to the cloud while keeping sensitive data on-site.
Security and Compliance: Ideal for industries with strict data privacy regulations.
Considerations:
Complexity: Managing a hybrid ERP solution can be more complex than choosing a purely cloud-based or on-premises system.
Industry-Specific SMB ERP:
Definition: Industry-specific ERP solutions are designed to meet the unique needs of particular industries, such as healthcare, manufacturing, or retail. They come with preconfigured modules and features tailored to those industries.
Advantages:
Customization: These solutions often require less customization since they are built with industry-specific needs in mind.
Compliance: They typically include compliance features specific to the industry.
Efficiency: Streamlined processes cater to the unique requirements of the industry.
Considerations:
Limited Versatility: Industry-specific ERP systems may not be suitable for businesses that span multiple sectors.
Open-Source SMB ERP:
Definition: Open-source ERP solutions provide access to the source code, allowing businesses to modify and customize the software according to their needs.
Advantages:
Cost-Effective: Open-source ERP is often more cost-effective in terms of licensing fees.
Flexibility: You have the freedom to customize and adapt the software to your unique requirements.
Community Support: A community of developers and users often provides support and updates.
Considerations:
Technical Expertise: Customization and management may require technical expertise, or you may need to hire developers.
Choosing the right SMB ERP solution depends on your specific business size, industry, budget, and customization needs. Consider the pros and cons of each type to make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals.
How to Choose the Right SMB ERP System
Selecting the right SMB ERP system is critical. Consider factors like your business size, industry, scalability, and customization options. It’s advisable to consult with an ERP expert to make an informed decision.
Implementing SMB ERP: Best Practices
Successful implementation involves thorough planning, employee training, and change management. It’s essential to define your objectives and establish key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring success.
Customization and Integration of SMB ERP
Tailor the ERP system to your specific business processes. Integration with other software and tools can enhance functionality and data exchange.
SMB ERP Case Studies
Explore real-world examples of SMBs that have benefited from ERP implementation. Learn from their experiences and best practices.
Cost Considerations for SMB ERP
While SMB ERP is cost-effective compared to traditional ERP, it’s essential to budget for initial setup, ongoing maintenance, and possible customization.
Challenges and Solutions in SMB ERP Implementation
SMBs may face challenges during ERP implementation, such as data migration or resistance to change. Identifying potential roadblocks and finding solutions is crucial.
Future Trends in SMB ERP
Stay updated with the latest trends in SMB ERP, such as AI and machine learning integration, enhanced mobility, and advanced analytics.
Security in SMB ERP
Protecting your data and sensitive customer information is paramount. Ensure that your SMB ERP system has robust security features.
User Training and Support
Invest in employee training to maximize the benefits of your ERP system. Adequate support and resources should be available for users.
ROI and Business Growth with SMB ERP
Measure the return on investment and track business growth after implementing SMB ERP. It’s a testament to the system’s effectiveness.
FAQs
What is SMB ERP?
SMB ERP stands for Small and Medium Business Enterprise Resource Planning, a software solution designed to manage and integrate various aspects of an SMB’s operations.
Why is SMB ERP important for small businesses?
SMB ERP streamlines operations, improves efficiency, and provides real-time insights, empowering SMBs to compete with larger enterprises.
How can SMBs choose the right ERP system?
Choosing the right SMB ERP system involves considering factors like business size, industry, scalability, and customization options.
What are the typical challenges in SMB ERP implementation?
Challenges may include data migration, resistance to change, and the need for thorough employee training.
How can SMBs measure the ROI of ERP implementation?
SMBs can measure the return on investment and track business growth to assess the effectiveness of their SMB ERP system.
Conclusion
SMB ERP has become a game-changer for small and medium businesses, offering the tools and insights necessary to compete in a dynamic marketplace. As SMBs continue to embrace these solutions, the future looks promising, with innovation and growth on the horizon.